Spring Boot 系列:Vue+Sping Boot +WebSocket实现前后端消息推送
目录
1.需求
2.原理
2.1握手协议:
2.2优点
3.步骤
3.1后端springboot集成websocket
3.2新建配置类, 开启WebSocket支持
3.3新建WebSocketServer服务端
3.4前端
3.5编写访问接口模仿服务端消息推送
3.6服务端推送对象数据(WebSocket-发送对象-自定义Encoder)
3.7结果
4异常
1.需求
前后端实现数据实时传输,采用长连接的模式 websocket
前端vue项目,后端Springboot
2.原理
WebSocket是一种在单个TCP连接上进行全双工通信的协议。WebSocket通信协议于2011年被IETF定为标准RFC 6455,并由RFC7936补充规范。WebSocketAPI也被W3C定为标准。
WebSocket使得客户端和服务器之间的数据交换变得更加简单,允许服务端主动向客户端推送数据。在WebSocket API中,浏览器和服务器只需要完成一次握手,两者之间就直接可以创建持久性的连接,并进行双向数据传输。
2.1握手协议:
WebSocket 是独立的、创建在 TCP 上的协议。
Websocket 通过HTTP/1.1 协议的101状态码进行握手。
为了创建Websocket连接,需要通过浏览器发出请求,之后服务器进行回应,这个过程通常称为“握手”(handshaking)。
2.2优点
优点:
- 较少的控制开销。在连接创建后,服务器和客户端之间交换数据时,用于协议控制的数据包头部相对较小。在不包含扩展的情况下,对于服务器到客户端的内容,此头部大小只有2至10字节(和数据包长度有关);对于客户端到服务器的内容,此头部还需要加上额外的4字节的掩码。相对于HTTP请求每次都要携带完整的头部,此项开销显著减少了。
- 更强的实时性。由于协议是全双工的,所以服务器可以随时主动给客户端下发数据。相对于HTTP请求需要等待客户端发起请求服务端才能响应,延迟明显更少;即使是和Comet等类似的长轮询比较,其也能在短时间内更多次地传递数据。
- 保持连接状态。与HTTP不同的是,Websocket需要先创建连接,这就使得其成为一种有状态的协议,之后通信时可以省略部分状态信息。而HTTP请求可能需要在每个请求都携带状态信息(如身份认证等)。
- 更好的二进制支持。Websocket定义了二进制帧,相对HTTP,可以更轻松地处理二进制内容。
- 可以支持扩展。Websocket定义了扩展,用户可以扩展协议、实现部分自定义的子协议。如部分浏览器支持压缩等。
- 更好的压缩效果。相对于HTTP压缩,Websocket在适当的扩展支持下,可以沿用之前内容的上下文,在传递类似的数据时,可以显著地提高压缩率。
3.步骤
3.1后端springboot集成websocket
gradle中集成websocket
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web'
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-websocket'
3.2新建配置类, 开启WebSocket支持
WebSocketConfig.java
package com.trgis.config;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnWebApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.socket.server.standard.ServerEndpointExporter;
/**
* 开启WebSocket支持
**/
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnWebApplication
public class WebSocketConfig {
//使用boot内置tomcat时需要注入此bean
@Bean
public ServerEndpointExporter serverEndpointExporter() {
return new ServerEndpointExporter();
}
}
3.3新建WebSocketServer服务端
WebSocket.java
@ServerEndpoint("/websocket")
@Component
@Slf4j
public class WebSocket {
//与某个客户端的连接会话,需要通过它来给客户端发送数据
private Session session;
//concurrent包的线程安全Set,用来存放每个客户端对应的WebSocket对象。
private static CopyOnWriteArraySet<WebSocket> webSocketSet=new CopyOnWriteArraySet<>();
/**
* 建立连接成功
* @param session
*/
@OnOpen
public void onOpen(Session session){
this.session=session;
webSocketSet.add(this);
log.info("【websocket消息】 有新的连接,总数{}",webSocketSet.size());
}
/**
* 连接关闭
*/
@OnClose
public void onClose(){
this.session=session;
webSocketSet.remove(this);
log.info("【websocket消息】 连接断开,总数{}",webSocketSet.size());
}
/**
* 接收客户端消息
* @param message
*/
@OnMessage
public void onMessage(String message){
log.info("【websocket消息】 收到客户端发来的消息:{}",message);
}
/**
* 发送消息
* @param message
*/
public void sendMessage(String message){
log.info("【websocket消息】 发送消息:{}",message);
for (WebSocket webSocket:webSocketSet){
try {
webSocket.session.getBasicRemote().sendText(message);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}@ServerEndpoint 注解是一个类层次的注解,它的功能主要是将目前的类定义成一个websocket服务器端。注解的值将被用于监听用户连接的终端访问URL地址。
onOpen 和 onClose 方法分别被@OnOpen和@OnClose 所注解。他们定义了当一个新用户连接和断开的时候所调用的方法。
onMessage 方法被@OnMessage所注解。这个注解定义了当服务器接收到客户端发送的消息时所调用的方法。
用onMessage()接收前端用户发来的消息。
用sendMessage()给前端用户发送消息。
注意@ServerEndpoint("/websocket")是你连接时的url,如果后端为192.168.1.88:9997,那么前端websocket连接url写为: ws:http://192.168.1.88:9997/websocket
3.4前端
<template>
<div class="Task">
<div class="" style="height: 100px;width: 100px;color: #fff;" >
<button @click="close()">关闭连接</button>
<input type="text" id="name" v-model="message"/><button @click="send()">发送消息</button>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import {baseURL} from 'src/const/config'
export default {
name: "Task",
data(){
return{
baseURL,
websock: null,
message: "",
}
},
mounted() {
this.initWebSocket()
},
methods:{
initWebSocket(){ //初始化weosocket
const wsuri = 'ws://192.168.1.88:9997/websocket';//ws地址
this.websock = new WebSocket(wsuri);
this.websock.onopen = this.websocketonopen;
this.websock.onerror = this.websocketonerror;
this.websock.onmessage = this.websocketonmessage;
this.websock.onclose = this.websocketclose;
},
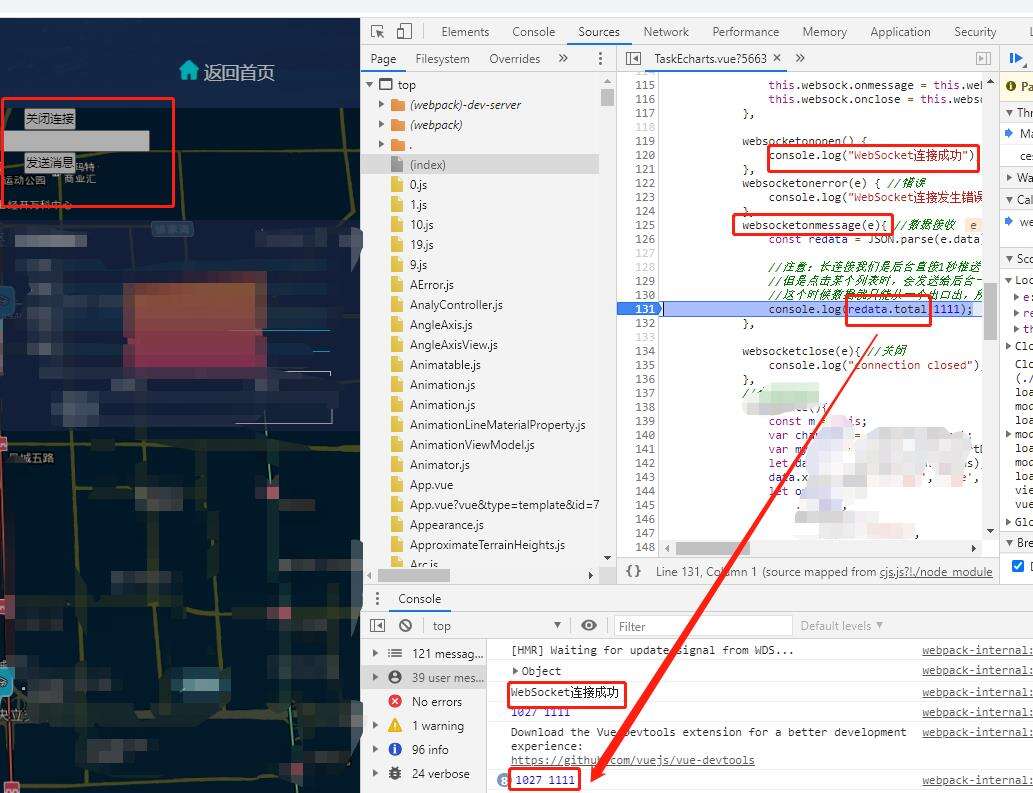
websocketonopen() {
console.log("WebSocket连接成功");
websocket.send(""WebSocket连接成功");//发送消息
},
websocketonerror(e) { //错误
console.log("WebSocket连接发生错误");
},
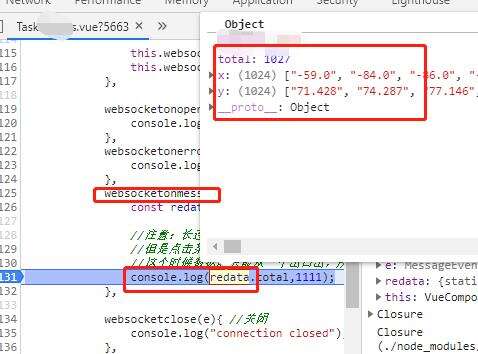
websocketonmessage(e){ //数据接收
const redata = JSON.parse(e.data);//接收对象的
//注意:长连接我们是后台直接1秒推送一条数据,
//但是点击某个列表时,会发送给后台一个标识,后台根据此标识返回相对应的数据,
//这个时候数据就只能从一个出口出,所以让后台加了一个键,例如键为1时,是每隔1秒推送的数据,为2时是发送标识后再推送的数据,以作区分
console.log(redata.total,1111);
},
websocketclose(e){ //关闭
console.log("connection closed");
},
close(){
// this.websocketclose();
this.websock.onclose;
},
send(){
this.websock.send(message);
},
},
destroyed: function() {
//页面销毁时关闭长连接
this.websocketclose();
},
}
</script>
<style scoped lang="less">
</style>
3.5编写访问接口模仿服务端消息推送
/**
* 发送场景模拟
* @param msg
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("/send")
@ResponseBody
public String sendMessage(String msg) {
//如果访问的地址中msg参数不为空值,发送msg的值给前端
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(msg)) {
webSocket.sendMessage(msg);
return "服务端发送消息:" + msg;
}
return "服务端未发送消息:" + msg;
}3.6服务端推送对象数据(WebSocket-发送对象-自定义Encoder)
Websocket发送对象,通过Encoder 自定义规则(转换为JSON字符串),前端收到后再转换为JSON对象
3.6.1自定义Encoder
package com.trgis.config;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import com.trgis.vo.SocketVO;
import javax.websocket.Encoder;
import javax.websocket.EndpointConfig;
import java.util.Map;
public class WebSocketCustomEncoding implements Encoder.Text<SocketVO> {
@Override
public String encode(SocketVO vo) {
assert vo!=null;
return JSON.toJSONString(vo);
}
@Override
public void init(EndpointConfig endpointConfig) {
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
}
}3.6.2 SocketVo
package com.trgis.vo;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiModelProperty;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import java.util.ArrayList;
/**
* @PackageName: com.trgis.vo
* @ClassName: socketVO
* @Author: zoe
* @Date: 2021/4/9 0013 11:02
* @Description: socket对象 传给前端
*/
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class SocketVO {
@ApiModelProperty("名称")
private String name;
@ApiModelProperty("总计条数")
private Integer total;
@ApiModelProperty("x")
private ArrayList<String> x;
@ApiModelProperty("y")
private ArrayList<String> y;
}
3.6.3 Websocket发送自定义对象
在@ServerEndpoint 指定endocers
修改刚刚的webSocket.java中的WebSocket中的@ServerEndpoint 并增加sendMessage(SocketVO vo)方法 代表返回对象
@ServerEndpoint(value = "/websocket",encoders = WebSocketCustomEncoding.class)
@Component
@Slf4j
public class WebSocket {
/**
* 新增 发送消息 对象模式
* @param vo
*/
public void sendMessage(SocketVO vo){
log.info("【websocket消息】 发送消息:{}",vo);
for (WebSocket webSocket:webSocketSet){
try {
webSocket.session.getBasicRemote().sendObject(vo);
} catch (IOException | EncodeException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}如果不在 @ServerEndpoint 指定endocers,直接通过sendObject(Object o)发送对象,
会报javax.websocket.EncodeException: No encoder specified for object of class xxxx异常
3.6.4Controll中调用修改
/**
* 发送场景模拟
* @param msg
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("/send")
@ResponseBody
public String sendMessage(String msg) {
//如果访问的地址中msg参数不为空值,发送msg的值给前端
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(msg)) {
//webSocket.sendMessage(msg);
SocketVO vo = new SocketVO();
vo.setX("x");
vo.setY("y");
vo.setName(msg);
vo.setTotal(10);
socket.sendMessage(vo);
return "服务端发送消息:" + msg;
}
return "服务端未发送消息:" + msg;
}3.7结果
4异常
可能遇到的错误及注意事项:
检查new WebSocket("ws://localhost:9997/websocket");的路径是否正确、是否以ws://开头,端口是否对应正确
url是否和后端配置的一致,单词是否拼写正确,导包是否正确
前后端端口号是否重复占用
gradle引包是否正确
tomcat是否使用7以上版本,建议使用tomcat8以及较新的springboot版本
后端配置文件是否注入spring
是否设置了拦截器
