fastjson转换对象实体@JsonProperty不生效问题及解决
fastjson转换对象实体@JsonProperty不生效
项目场景
请求第三方应用 返回json数据
问题描述
第三方返回的数据中,存在java关键词,无法直接使用原属性名进行对应 例如(class、interface等)使用@JsonProperty注解不能返回正确的结果
@Data
static class User{
@JsonProperty( "class")
private String userClass;
@JsonProperty("interface")
private String userInterface;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("class","测试");
map.put("interface","测试1");
String mapStr = JSONObject.toJSONString(map);
System.out.println(mapStr);
User user = JSONObject.parseObject(mapStr, User.class);
System.out.println(user);
}正常情况来讲 @JsonProperty 注解完全够用,可以成功解析出想要的结果。
但往往事情并不是那么简单
执行结果 :
{"interface":"测试1","class":"测试"}
User(userClass=null, userInterface=null)
可以看出并没有成功映射到想要的数据
原因分析
具体原因感兴趣的同学可以看下 JSONObject.parseObject 的源码
解决方案
解决方法有两种
1、修改属性名称,使用原属性名 + “_”
@Data
static class User{
@JsonProperty( "class")
private String class_;
@JsonProperty("interface")
private String interface_;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("class","测试");
map.put("interface","测试1");
String mapStr = JSONObject.toJSONString(map);
System.out.println(mapStr);
User user = JSONObject.parseObject(mapStr, User.class);
System.out.println(user);
}执行结果 :
{"interface":"测试1","class":"测试"}
User(class_=测试, interface_=测试1)
2、使用fastjson @JSONField注解
@Data
static class User{
@JSONField(name = "class")
private String userClass;
@JSONField(name = "interface")
private String userInterface;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("class","测试");
map.put("interface","测试1");
String mapStr = JSONObject.toJSONString(map);
System.out.println(mapStr);
User user = JSONObject.parseObject(mapStr, User.class);
System.out.println(user);
}执行结果:
{"interface":"测试1","class":"测试"}
User(userClass=测试, userInterface=测试1)
@JsonProperty 失效问题的排查
@JsonProperty 是Jackson提供的一个用于注解属性、类、方法等的json注解。使用它可以改变Json序列化时属性的名称,一般默认使用属性名,比如如下的代码示例,如果没有使用@JsonProperty注解那么id转化为json为{“id”:11}.使用了则就是{“Id”:11}.
@JsonInclude(Include.NON_NULL)
public class User implements Serializable {
@JsonProperty("Id")
private Integer id;
@JsonProperty("Name")
private String name;
@JsonProperty("pwd")
private Integer passWord;
}在一次使用springboot项目时发现@JsonProperty不生效。
那么是因为啥呢?
因为在项目里还引用了fastJson,在debug时发现接口最后响应时是使用FastJson做json序列化。
解决方法:
使用@EnableWebMvc注解,加在启动类上。或者直接在项目里不引用fastJson.
@EnableWebMvc
public class SpringBootMain extends SpringBootServletInitializer implements WebApplicationInitializer {
@Override
protected SpringApplicationBuilder configure(SpringApplicationBuilder application) {
return application.sources(SpringBootMain.class);
}
}springboot 是如何选择使用json序列化工具的呢?即如何调用jackson进行json序列化和反序列化?
springboot 通过HttpMessageConverters 消息转换器通过jackson将java对象转化为json字符串。如果项目里包含多个json工具包比如jackson ,fastjson,那么就会各个年级对象的内容选择一个合适的去转换为json。
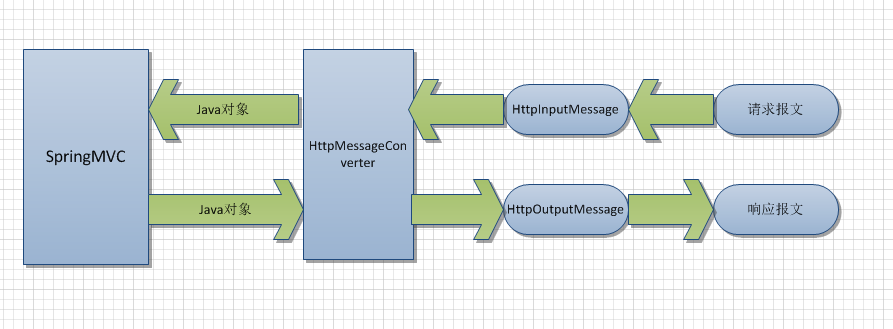
这是HttpMessageConverters 消息转换器所处的位置,所以项目里采用那个json工具由该类决定。
springboot默认使用jackson,springboot默认集成的就是jackson。
指定使用fastJson的一种做法:
public class SpringBootMain extends SpringBootServletInitializer implements WebApplicationInitializer {
@Bean
public HttpMessageConverters fastJsonHttpMessageConverters() {
// 1.定义一个converters转换消息的对象
FastJsonHttpMessageConverter fastConverter = new FastJsonHttpMessageConverter();
// 2.添加fastjson的配置信息,比如: 是否需要格式化返回的json数据
FastJsonConfig fastJsonConfig = new FastJsonConfig();
fastJsonConfig.setSerializerFeatures(SerializerFeature.PrettyFormat);
// 3.在converter中添加配置信息
fastConverter.setFastJsonConfig(fastJsonConfig);
// 4.将converter赋值给HttpMessageConverter
HttpMessageConverter<?> converter = fastConverter;
// 5.返回HttpMessageConverters对象
return new HttpMessageConverters(converter);
}
}以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持编程学习网。
