使用C#实现数据结构堆的代码
一、 堆的介绍:
堆是用来排序的,通常是一个可以被看做一棵树的数组对象。堆满足已下特性:
1. 堆中某个节点的值总是不大于或不小于其父节点的值
任意节点的值小于(或大于)它的所有后裔,所以最小元(或最大元)在堆的根节点上(堆序性)。堆有大根堆和小根堆,将根节点最大的堆叫做最大堆或大根堆,根节点最小的堆叫做最小堆或小根堆。
2. 堆总是一棵完全二叉树
除了最底层,其他层的节点都被元素填满,且最底层尽可能地从左到右填入。
堆示意图:

将堆元素从上往下从左到右放进数组对象中,子父节点索引满足关系:
parentIndex = (index+1)/ 2 - 1;
childLeftIndex = parentIndex * 2 + 1;
childRightIndex = (parentIndex + 1) * 2;
其中:index为任一节点索引;parentIndex该节点父索引;childLeftIndex该父节点下的子左节点;childRightIndex该父节点下的子右节点。
创建堆的大概思路:
1. 向堆中添加元素:
加到数组尾处,循环比对其父节点值(大根堆和小根堆比对策略不一样),比对结果的目标索引不是父节点索引则交换子父节点元素,继续向上比对其父父节点…;直至比对过程中目标索引为父节点索引或达到根节点结束,新堆创建完成。
2. 向堆中取出元素:
取出根节点元素,并将堆末尾元素插入根节点(为了保证堆的完全二叉树特性),从根部再循环向下比对父节点、子左节点、子右节点值,比对结果目标索引不为父节点交换目标索引和父节点的值,向下继续比对;直至比对过程中目标索引为父节点索引或达到堆尾部结束,新堆创建完成。
二、 代码实现:
因为大根堆和小根堆只是比较策略不同,所以整合了两者,用的时候可以直接设置堆的类别;默认小根堆,默认比较器。实现代码如下:
public class Heap<T>
{
private T[] _array;//数组,存放堆数据
private int _count;//堆数据数量
private HeapType _typeName;//堆类型
private const int _DefaultCapacity = 4;//默认数组容量/最小容量
private const int _ShrinkThreshold = 50;//收缩阈值(百分比)
private const int _MinimumGrow = 4;//最小扩容量
private const int _GrowFactor = 200; // 数组扩容百分比,默认2倍
private IComparer<T> _comparer;//比较器
private Func<T, T, bool> _comparerFunc;//比较函数
//堆数据数量
public int Count => _count;
//堆类型
public HeapType TypeName => _typeName;
public Heap() : this(_DefaultCapacity, HeapType.MinHeap, null) { }
public Heap(int capacity) : this(capacity, HeapType.MinHeap, null) { }
public Heap(HeapType heapType) : this(_DefaultCapacity, heapType, null) { }
public Heap(int capacity, HeapType heapType, IComparer<T> comparer)
{
Init(capacity, heapType, comparer);
}
public Heap(IEnumerable<T> collection, HeapType heapType, IComparer<T> comparer)
{
if (collection == null)
throw new IndexOutOfRangeException();
Init(collection.Count(), heapType, comparer);
using (IEnumerator<T> en = collection.GetEnumerator())//避免T在GC堆中有非托管资源,GC不能释放,需手动
{
while (en.MoveNext())
Enqueue(en.Current);
}
}
private void Init(int capacity, HeapType heapType, IComparer<T> comparer)
{
if (capacity < 0)
throw new IndexOutOfRangeException();
_count = 0;
_array = new T[capacity];
_comparer = comparer ?? Comparer<T>.Default;
_typeName = heapType;
switch (heapType)
{
default:
case HeapType.MinHeap:
_comparerFunc = (T t1, T t2) => _comparer.Compare(t1, t2) > 0;//目标对象t2小
break;
case HeapType.MaxHeap:
_comparerFunc = (T t1, T t2) => _comparer.Compare(t1, t2) < 0;//目标对象t2大
break;
}
}
public T Dequeue()
{
if (_count == 0)
throw new InvalidOperationException();
T result = _array[0];
_array[0] = _array[--_count];
_array[_count] = default(T);
if (_array.Length > _DefaultCapacity && _count * 100 <= _array.Length * _ShrinkThreshold)//缩容
{
int newCapacity = Math.Max(_DefaultCapacity, (int)((long)_array.Length * (long)_ShrinkThreshold / 100));
SetCapacity(newCapacity);
}
AdjustHeap(_array, 0, _count);
return result;
}
public void Enqueue(T item)
{
if (_count >= _array.Length)//扩容
{
int newCapacity = Math.Max(_array.Length+_MinimumGrow, (int)((long)_array.Length * (long)_GrowFactor / 100));
SetCapacity(newCapacity);
}
_array[_count++] = item;
int parentIndex;
int targetIndex;
int targetCount = _count;
while (targetCount > 1)
{
parentIndex = targetCount / 2 - 1;
targetIndex = targetCount - 1;
if (!_comparerFunc.Invoke(_array[parentIndex], _array[targetIndex]))
break;
Swap(_array, parentIndex, targetIndex);
targetCount = parentIndex + 1;
}
}
private void AdjustHeap(T[] array, int parentIndex, int count)
{
if (_count < 2)
return;
int childLeftIndex = parentIndex * 2 + 1;
int childRightIndex = (parentIndex + 1) * 2;
int targetIndex = parentIndex;
if (childLeftIndex < count && _comparerFunc.Invoke(array[parentIndex], array[childLeftIndex]))
targetIndex = childLeftIndex;
if (childRightIndex < count && _comparerFunc.Invoke(array[targetIndex], array[childRightIndex]))
targetIndex = childRightIndex;
if (targetIndex != parentIndex)
{
Swap(_array, parentIndex, targetIndex);
AdjustHeap(_array, targetIndex, _count);
}
}
private void SetCapacity(int capacity)
{
T[] newArray = new T[capacity];
Array.Copy(_array, newArray, _count);
_array = newArray;
}
private void Swap(T[] array, int index1, int index2)
{
T temp = array[index1];
array[index1] = array[index2];
array[index2] = temp;
}
public void Clear()
{
Array.Clear(_array, 0, _count);
Init(_DefaultCapacity, HeapType.MinHeap, null);
}
}
public enum HeapType { MinHeap, MaxHeap }三、 使用测试:
建一个Person类用来测试,例子中Person比较规则是:先按年龄比较,年龄相同再按身高比较。具体比较大小是由选择堆的类别进行不同的排序规则:如Person类中小根堆先按年龄小者排序,年龄相同者按身高大者排序;而使用大根堆则相反。两种比较器写法,前者直接使用默认比较器;后者需要将比较器注入到堆中。
public class Person : IComparable<Person>
{
public string name { get; set; }
public int Age { get; set; }
public int Height { get; set; }
public override string ToString()
{
return $"我叫{name},年龄{Age},身高{Height}";
}
//小根堆:先排年龄小,年龄相同,按身高大的先排;大根堆相反
public int CompareTo(Person other)
{
if (this.Age.CompareTo(other.Age) != 0)
return this.Age.CompareTo(other.Age);
else if (this.Height.CompareTo(other.Height) != 0)
return ~this.Height.CompareTo(other.Height);
else
return 0;
}
}
public class personComparer : IComparer<Person>
{
//大根堆:先排年龄大,年龄相同,按身高大的先排;小根堆相反
public int Compare(Person x, Person y)
{
if (x.Age.CompareTo(y.Age) != 0)
return x.Age.CompareTo(y.Age);
else if (x.Height.CompareTo(y.Height) != 0)
return x.Height.CompareTo(y.Height);
else
return 0;
}
}主函数调用:
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] array = { 3, 5, 8, 3, 7, 1 };
Heap<int> heap0 = new Heap<int>(array, HeapType.MaxHeap, null);
Console.WriteLine(heap0.TypeName);
Console.WriteLine(heap0.Dequeue());
Console.WriteLine(heap0.Dequeue());
Console.WriteLine(heap0.Dequeue());
Console.WriteLine(heap0.Dequeue());
int length = heap0.Count;
for (int count = 0; count < length; count++)
{
Console.WriteLine(heap0.Dequeue());
}
Person person1 = new Person() { Age = 12, Height = 158, name = "张三" };
Person person2 = new Person() { Age = 13, Height = 160, name = "李四" };
Person person3 = new Person() { Age = 10, Height = 150, name = "王二" };
Person person4 = new Person() { Age = 10, Height = 152, name = "麻子" };
Person person5 = new Person() { Age = 12, Height = 150, name = "刘五" };
List<Person> people = new List<Person>();
people.Add(person1);
people.Add(person2);
people.Add(person3);
people.Add(person4);
people.Add(person5);
Heap<Person> heap2 = new Heap<Person>(people, HeapType.MinHeap, null);
Person person6 = new Person() { Age = 9, Height = 145, name = "赵六" };
heap2.Enqueue(person6);
Console.WriteLine(heap2.TypeName);
Console.WriteLine(heap2.Dequeue());
Console.WriteLine(heap2.Dequeue());
Console.WriteLine(heap2.Dequeue());
Console.WriteLine(heap2.Dequeue());
PersonComparer personComparer = new PersonComparer();
Heap<Person> heap3 = new Heap<Person>(1,HeapType.MaxHeap,personComparer);
heap3.Enqueue(person1);
heap3.Enqueue(person2);
heap3.Enqueue(person3);
heap3.Enqueue(person4);
heap3.Enqueue(person5);
heap3.Enqueue(person6);
Console.WriteLine(heap3.TypeName);
Console.WriteLine(heap3.Dequeue());
Console.WriteLine(heap3.Dequeue());
Console.WriteLine(heap3.Dequeue());
Console.WriteLine(heap3.Dequeue());
Console.ReadKey();
}输出结果:
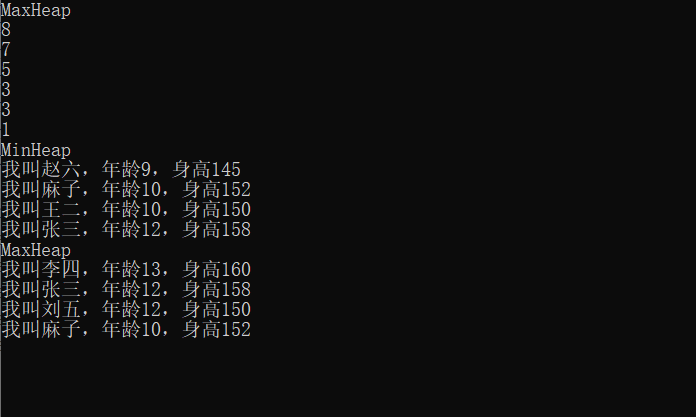
参考:
https://blog.csdn.net/qq826364410/article/details/79770791
https://docs.microsoft.com/zh-cn/dotnet/api/system.collections.generic.comparer-1?view=net-5.0
到此这篇关于使用C#实现数据结构堆的代码的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关C#实现数据结构堆内容请搜索得得之家以前的文章希望大家以后多多支持得得之家!
